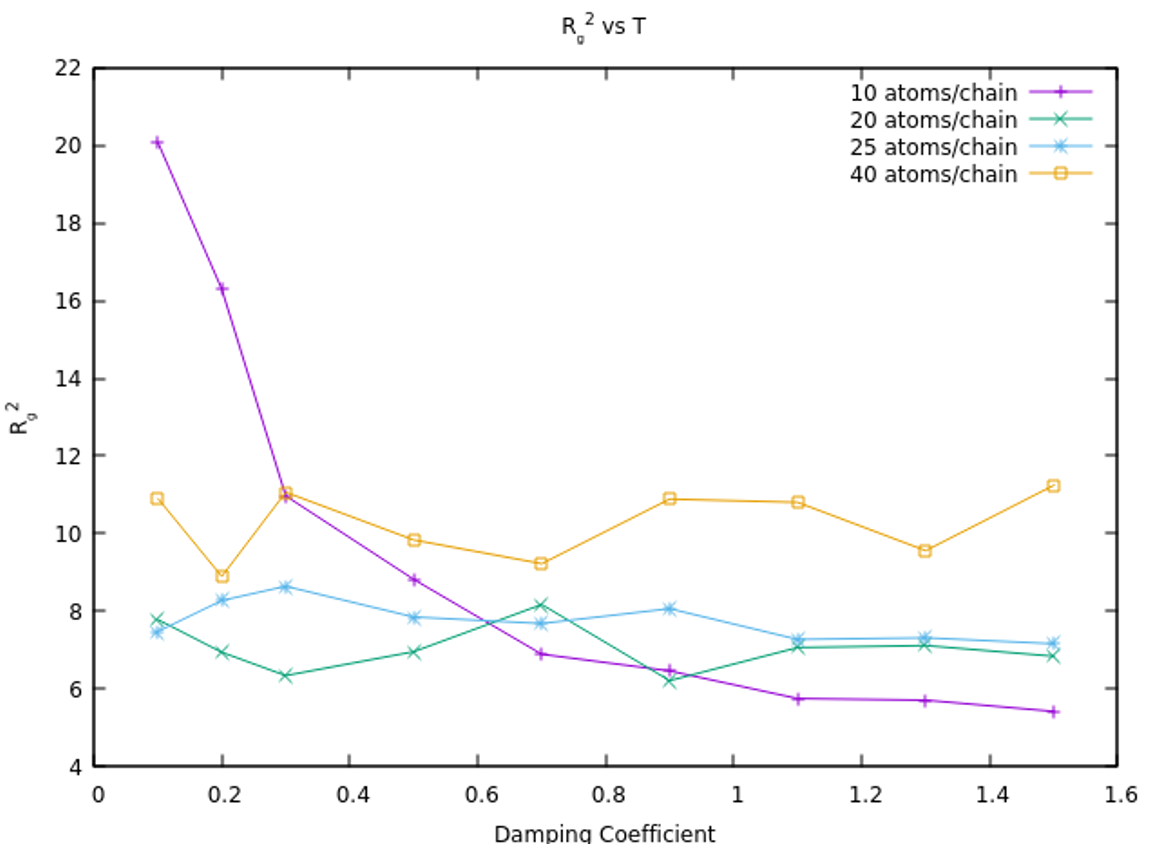
The project aims to simulate a coarse-grained linear polymer model
in an implicit solvent to analyze the behavior of the mean-squared
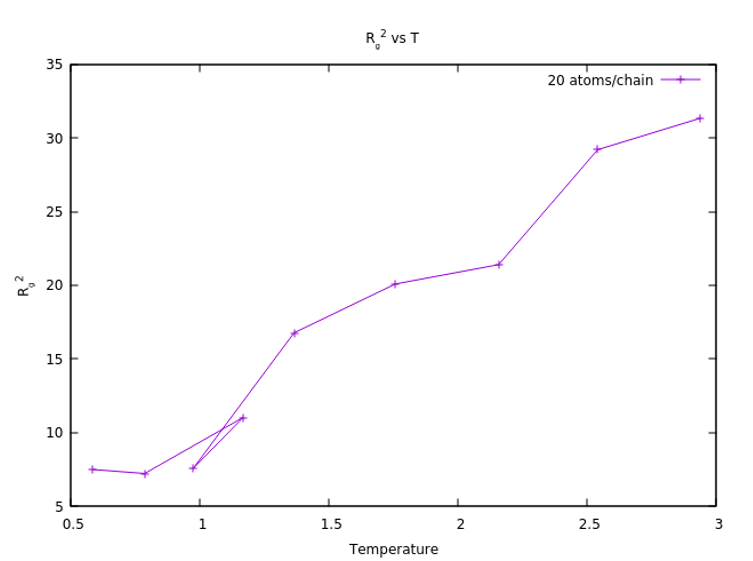
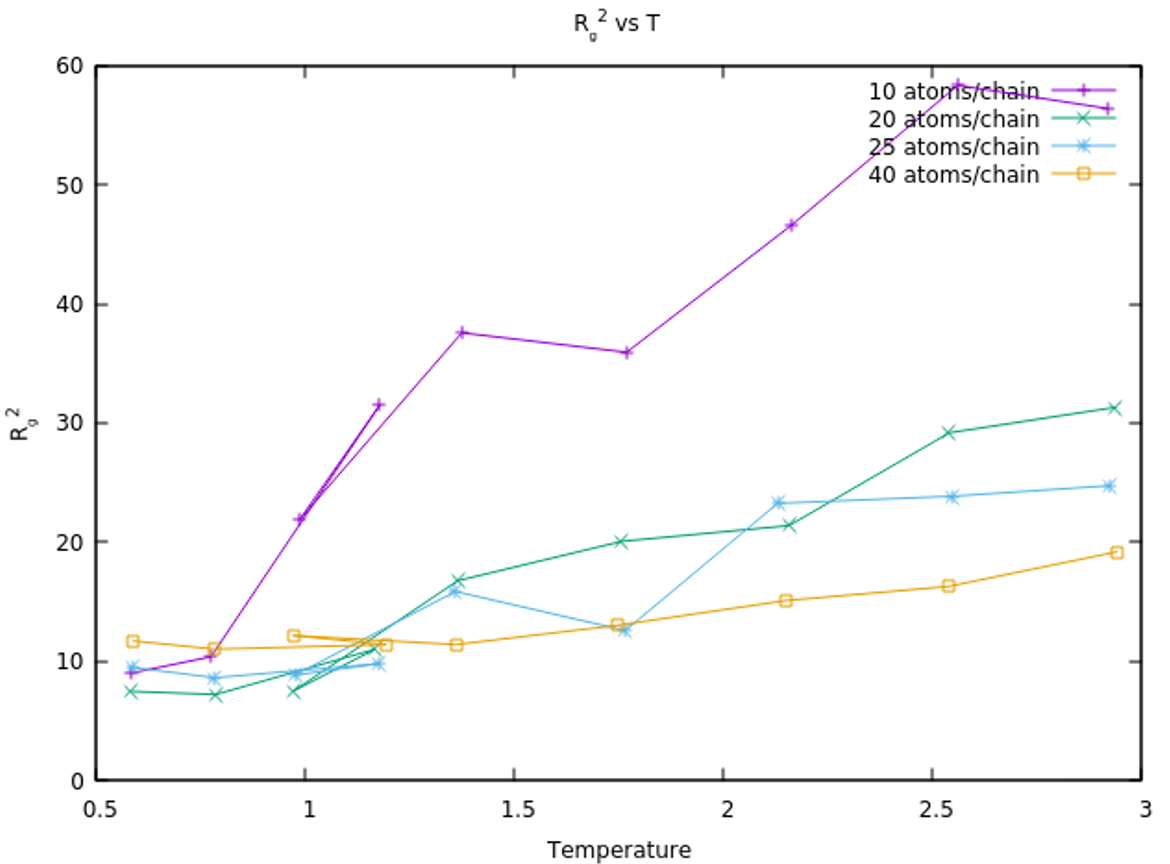
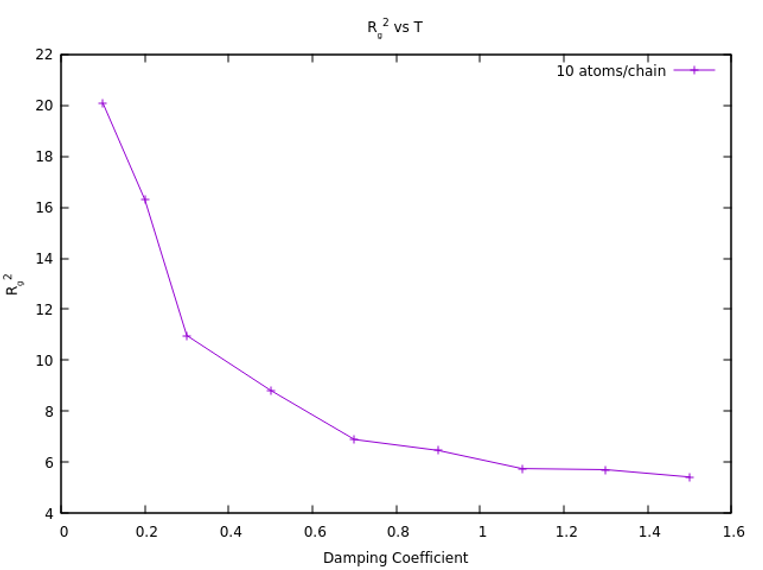
radius of gyration, Rg2, under
varying conditions of temperature and viscous forces. By
systematically adjusting these parameters, the simulation seeks to
identify the polymer system's θ-point. The approach
leverages the fact that in a coarse-grained polymer model with
N beads per chain, plotting Rg2
against temperature or damping coefficient for different N
values will yield curves that intersect at the θ-point.
This point represents the polymer's critical solubility behavior,
providing insight into the thermodynamic properties of polymer
solutions in various solvents.